| HG | 3,10 helix |
| HH | alpha helix |
| S(A/P/M)(Y/N) | beta sstrand, antiparallel/parallel/mixed, edge/not edge
(e.g. SAN = antiparallel strand not on edge) |
Difference between averages among the subclasses were qualified using the Student's t-test.
 |
 |
 |
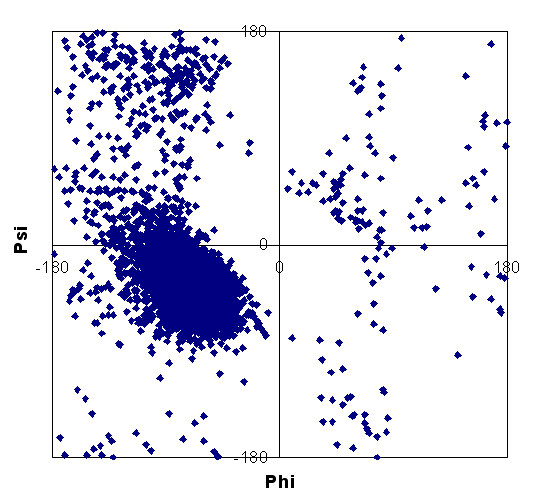
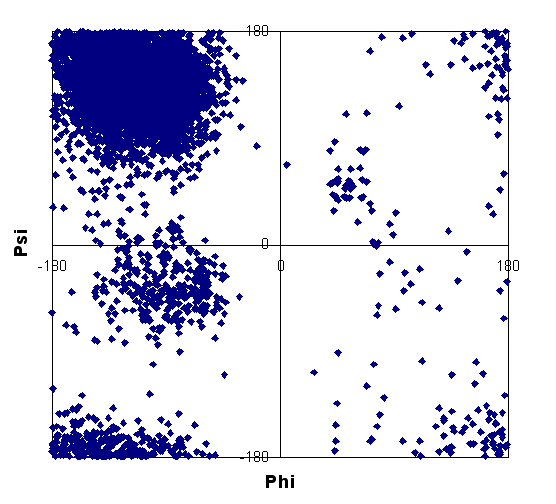
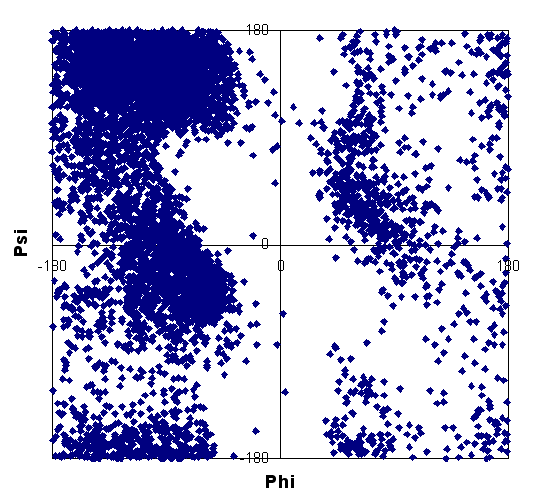
| helix | strand | non-helix, non-strand |
These plots show that some data points fall outside of expected regions for regular secondary structure. Such points were discarded from the data set used for calculations. Note that our database consists of a higher proportion of helix shift data compared to strand; this may be due to the bias toward NMR studies of all-helical or highly helical structures, with smaller, globular proteins often being of this nature.
Statistics for overall strand and subclasses
Statistical significance between subclasses
Note: amino acid type "B" refers to reduced cysteine, while "C" refers
to oxidized cysteine.
Chemical shift data plotted for the helix and strand subclasses show
that there is considerable difference particularly in Ca and CO shifts
between the alpha and 3,10 helix subclases; no significant differences
were found between
average secondary shifts of the different strand subclasses.
While differences are illustrated in the Ca and CO shifts for the two
helix subclasses, the absence of such trends in the strand subclasses may
not necessarily indicate that type of beta strand does not influence backbone
chemical shift, and may instead be due to the limited amount of data available
for parallel and mixed strand types. Such analysis should be repeated
with a database consisting of a higher proportion of strand shifts.