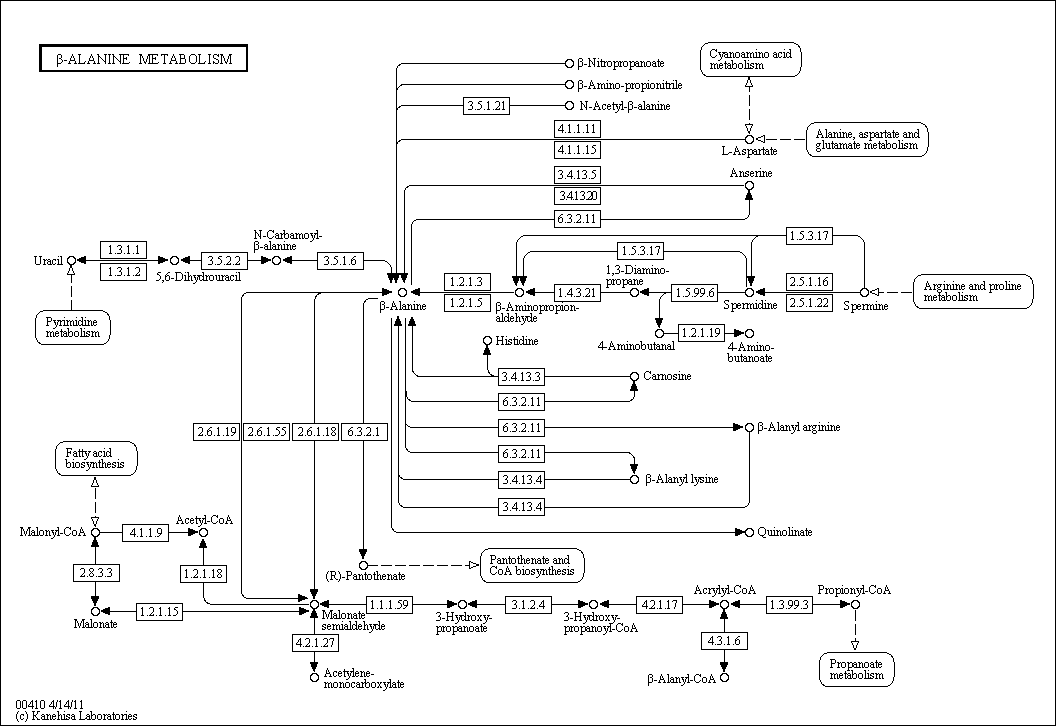
beta-Alanine Metabolism
Description: Beta-Alanine is a naturally occuring amino acid. Beta-Alanine is formed through the degradation of beta-alanine and its dipeptides. The dipeptides are found in protein rich foods such as meats, eggs, and peanut butter. Beta-alanine is also found and formed in the liver. The liver catabolizes pyrimidine nucleotides, breaking them down into uracil and dihydrouracil. They are then further metabolized to beta-alanine.
Beta-alanine is also formed during the dehydrogenase of various aliphatic polyamines. In general, beta-alanine is normally metabolized to acetic acid. Additionally, Beta-alanine is not used to synthesize any major proteins.
Related BMRB Molecules
- beta-Alanine
- 1,3-diaminopropane
- L-Anserine
- L-Aspartic Acid
- L-Histidine
- L-Carnosine
- Pantothenate
- Quinolinic-Acid
- Spermidine
- Spermine
- Uracil
- Dihydrouracil
- 3-Ureidopropionic-acid
For complete information about pathway, see KEGG [map00410]
