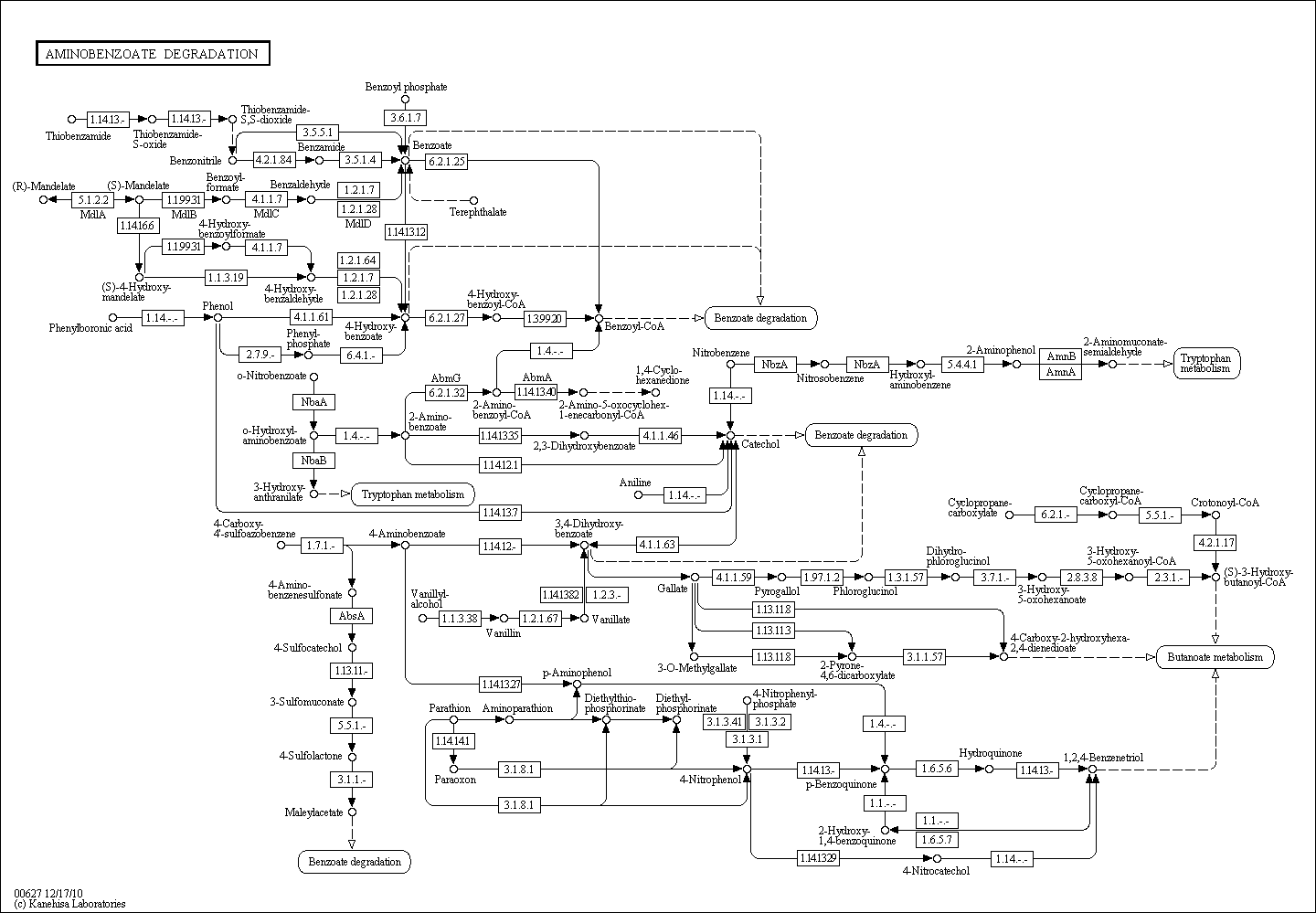
Aminobenzoate Degredation
Description: 2-Aminobenzoate is an intermediate derived from tryptophan and other indole ring-containing compounds. The catabolism of 2-aminobenzoate has largely been studied with aerobic bacteria. Its aerobic degradation is documented elsewhere in the UM-BBD. More recently, anaerobic catabolism of 2-Aminobenzoate has been studied and proceeds with initial esterification of the carboxyl group to coenzyme A (Altenschmidt et al., 1991). The subsequent proposed reduction of 2-aminobenzoyl-CoA to benzoyl-CoA is reminiscent of reductive deamination reported for the catabolism of nitroaromatic compounds, such as trinitrotoluene (TNT), following reduction of the nitro groups to form an aniline derivative (Lochmeyer et al., 1992). Source: University of Minnesota
Related BMRB Molecules
- Anthranilic-Acid
- 3-Hydroxyanthranilic-Acid
- 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
- Benzamide
- 1,2,4-Benzenetriol
- Nitrobenzene
- Nitrosobenzene
- Benzoate
- 4_aminobenzoic_acid
- 4-Hydroxybenzoic-Acid
- Benzonitrile
- Gallic-acid
- 1,4-Cyclohexanedione
- 4_hydroxy_3_methoxybenzyl_alcohol
- Phenol
- 2_Aminophenol
- 4-Aminophenol
- 4-Nitrophenol
- 4-Nitrophenyl-Phosphate
- 4-Nitrocatechol
- Hydroquinone
- Pyrocatechol
- Syringic Acid
- Vanillic-Acid
- Vanillin
For complete information about pathway, see KEGG [map00627]
